Understanding Cholesterol and Its Impact on Heart Health
High cholesterol and heart disease often go hand-in-hand. While cholesterol plays an essential role in the body’s daily functions, too much of the wrong kind can lead to serious health issues. Complete Cardiology Care can help you keep your cholesterol in check. Let us break down what cholesterol is, how it can affect your heart, and how to manage it effectively.
What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood. Your body needs it to build cells, produce hormones, and create vitamin D. However, not all cholesterol is the same. Understanding its differences is key to managing your heart health.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) – LDL is often referred to as “bad cholesterol.” It contributes to the buildup of fatty deposits in your arteries. These deposits, called plaques, can restrict blood flow and increase your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) – HDL, or “good cholesterol,” helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, carrying it back to the liver to be processed and eliminated. Higher HDL levels are often linked to a lower risk of heart disease.
- Triglycerides – These are another type of fat in your blood. High triglyceride levels combined with high LDL or low HDL levels significantly increase your risk of heart disease.
Normal vs. High Cholesterol Levels
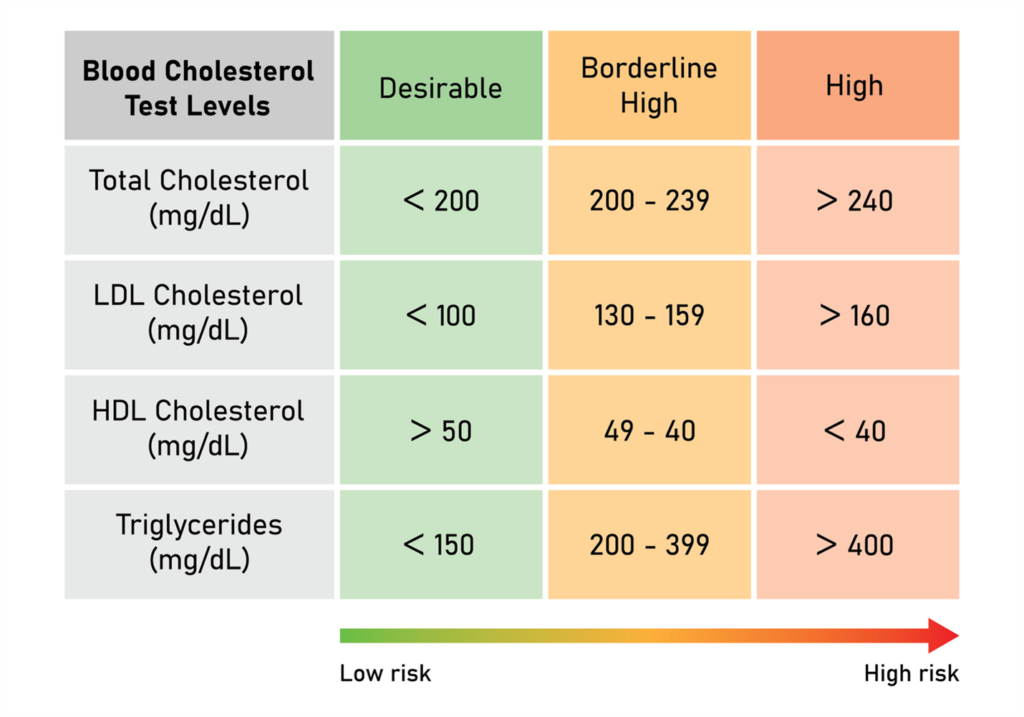
We measure cholesterol levels with a blood test called a lipid panel. This test examines your LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels. Below, we’ve listed what’s generally considered normal. Anything varying from these figures can put you at risk of heart issues:
- Total Cholesterol – Below 200 mg/dl
- LDL – Below 100 mg/dl
- HDL – 50 mg/dl or higher
- Triglycerides – Below 150 mg/dl
The Link Between High Cholesterol and Heart Disease
High cholesterol is a major contributor to heart disease. High LDL levels can lead to atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries. This condition limits blood flow and can cause heart complications such as:
- Heart Attack – Blocked arteries from high cholesterol can trigger a heart attack.
- Heart Palpitations – High cholesterol and heart palpitations are correlated because reduced blood flow to the heart can cause irregular heartbeats.
- Heart Disease – Cholesterol and heart disease risk are linked.
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol
Several factors contribute to high cholesterol, including
Lifestyle Factors
- Diet – Foods high in saturated fats and trans fats increase LDL levels.
- Exercise – Lack of physical activity can lower HDL levels and increase triglycerides.
- Smoking – Smoking damages your arteries and can lower HDL cholesterol.
Genetic Factors
Family history plays a significant role in cholesterol levels. If someone in your family has high cholesterol, you may be at greater risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is often called a silent condition because it typically has no symptoms. Many people only discover it after a serious event, like a heart attack or stroke. Regular blood tests are the best way to diagnose and monitor cholesterol levels.
Managing Cholesterol and Heart Disease Risk
There is good news regarding cholesterol. It can often be managed through simple lifestyle changes. We recommend:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins
- Exercising regularly
- Quitting smoking to reduce overall heart disease risk
Medications for Cholesterol Management
When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medications like statins can help lower LDL levels. Your doctor may also recommend other prescriptions, such as bile acid sequestrants or cholesterol absorption inhibitors.
Why Regular Checkups Matter
Routine heart assessments are vital for monitoring your cholesterol and heart health. Complete Cardiology Care can help. We offer comprehensive heart screenings and personalized treatment plans to help you manage your cholesterol and heart disease risk. Contact us today to schedule a consultation.